Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing life in the 21st century. It is changing the way we work, obtain information and make decisions. Hardly any other topic is currently being discussed so intensively in business, politics, science and society. While some celebrate technological progress, others see considerable risks.
To ensure that you have a say in the debate on artificial intelligence and that your company does not lose touch with the topic of AI, it is worth gaining a well-founded insight, which the following article offers.
Key take-aways #
- Artificial intelligence is based on algorithms, i.e. clear instructions for solving specific problems. It is trained with large amounts of data to recognize patterns and derive rules. In this way, it learns what makes the most sense under which conditions.
- Generative AI can generate new content (e.g. create texts, images or videos) by following the learned rules, calculating statistical probabilities from the training data and gradually selecting additional elements that best match the prompt.
- Unlike humans, weak AI systems cannot really think. They have no consciousness, no emotions, no morals and no intuition.
- Whether route planning, text correction or the personalized display of advertising – artificial intelligence is already omnipresent in everyday and professional life. It also plays an important role in research (e.g. climate models, early cancer detection).
- Problems that artificial intelligence can cause are: hallucination (inventing facts), amplification of discrimination, fraudulent activities, deepfakes, increasing energy consumption, data protection risks and dependence on technology corporations.

What is artificial intelligence? #
To date, there is no standard definition of artificial intelligence. From an economic point of view, however, it can be said that artificial intelligence is the ability of computer systems or machines to perform certain tasks that usually require human intelligence. At its core, current AI development is about recreating human abilities using statistical methods and algorithms. These include, among others:
- Processing information and storing it as knowledge
- Evaluating data and recognizing patterns
- Understanding and generating human language
- Solving problems, making decisions and acting socially
How does artificial intelligence differ from natural intelligence? #
Natural intelligence is created by neuronal processes in the human brain. It is inextricably linked to consciousness, emotions, creativity, morality and responsibility. Humans can transfer knowledge flexibly to new situations, act intuitively and grasp relationships, even when only little information is available.
Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, works data-based. It needs large amounts of data to imitate human intelligence, is not aware of what it is doing and does not think, but calculates statistical probabilities. It has no emotions, morals or intuition.
What types of artificial intelligence are there? #
Artificial intelligence is usually divided into the types strong and weak AI.
Weak AI #
Today, artificial intelligence almost always refers to weak AI. It specializes in performing clearly defined, recurring tasks particularly well.
However, weak AI cannot think, develop intentions or reflect on itself. It has no creativity and does not learn independently, but has to be trained. Its ability to learn is usually limited to the application of algorithms (clear instructions for solving certain problems) and to recognizing patterns in large amounts of data. This is particularly useful in rule-based automation of processes and in language and image processing.
Strong AI #
A so-called strong AI that fully emulates human thinking does not yet exist. A strong AI would not only carry out individual tasks on instruction, but could theoretically learn and develop independently, find creative solutions in completely new contexts, formulate goals and pursue strategies.
It is questionable whether such a hypothetical form of artificial intelligence could develop consciousness. In all probability, it would not have any real emotions, but only simulated emotions and no intuition, as its decisions would still be based on calculations. A strong AI could follow moral rules, but not feel moral responsibility like a human.
The Turing test as a criterion for artificial intelligence #
An important milestone in the history of AI is the Turing test, which was developed in 1950 by the British mathematician Alan Turing. He originally proposed a game to find out whether a machine or computer can deceive a human questioner in a comprehensive way and therefore possesses an ability to think on a par with humans.

This test was later reduced in its complexity, so that today the following test arrangement is known as the Turing test: A human test subject conducts a conversation with two unknown interlocutors via a keyboard and a screen. One interlocutor is a human, the other a machine. If the test person cannot reliably recognize which of the two is the machine through intensive questioning, the machine has passed the Turing test. We can therefore attribute weak artificial intelligence to the machine as soon as it demonstrates communication behavior on a par with humans.
How advanced is artificial intelligence today? #
Modern AI models – especially Large Language Models (LLM) – come very close to this definition of artificial intelligence in certain scenarios. Newer versions of ChatGPT have already passed the Turing test . They can simulate human communication in a text-based chat so skillfully that most people can no longer distinguish them from a real person and even mistake them for humans significantly more often than real human conversation partners.
However, ChatGPT’s AI model is not intelligent in the sense that it deliberately deceives and manipulates people. It only reliably calculates the probability of which answers the conversation partners are most likely to want to hear and which social behavior is considered appropriate in a certain situation. In other words, passing the Turing test does not mean that a machine really thinks, but merely that it imitates human behavior convincingly.
Typical technologies in the field of AI #
AI systems such as chatbots and voice assistants use basic procedures to imitate human abilities. These AI technologies include:
- Machine learning: AI systems learn to solve specific problems using statistical algorithms and a large amount of training data.
- Deep learning: Artificial neural networks with numerous layers enable the processing of particularly complex input data, for example in speech and facial recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Computers process and analyze natural language using algorithms, for example for text correction or text generation.
- Computer vision: Computers process and analyze images using algorithms, for example to recognize patterns and objects and create virtual worlds.
Where is artificial intelligence used? #
You have almost certainly already used artificial intelligence in everyday life – consciously or unconsciously. Whether for route planning in navigation systems, purchase recommendations in online stores or autocorrection and autocompletion of texts: Trained AI is in use everywhere, calculating the most likely solution for you from countless pieces of data in the background.
In medical research, artificial intelligence is already being used to improve diagnoses and image analysis, for example in the early detection of cancer. Researchers can also use artificial intelligence to simulate scenarios under certain assumptions, for example to calculate global warming using climate models or to use resources efficiently in agriculture. This clearly shows that AI technologies have great benefits for society.
Areas of application for AI in the economy #
Artificial intelligence is also used in many companies. As the performance of AI systems has increased rapidly in recent years, artificial intelligence can analyze enormous amounts of data in a short space of time and recognize correlations that are almost impossible for humans to grasp. AI helps to make informed decisions by recognizing developments at an early stage and simulating future scenarios. In office work in particular, many recurring tasks can also be automated with the help of AI. Here are some examples from different areas:
Industry and production #
- Forecasting demand and sales to optimize supply chains
- Predictive maintenance and servicing of machines
- Robotics and automated production lines

Marketing and sales #
- Personalized customer targeting in the display of advertising
- Faster content creation with generative AI
- Analysis of specific target groups for the marketing plan
HR and personnel development #
- Standardized interviews with virtual assistants
- Analysis of the qualifications and personality profiles of applicants
- Forecasts of personnel requirements in certain scenarios
General administration #
- Summarizing or writing reports, e-mails, etc.
- Creating quotations , order confirmations and invoices
- Answering support requests

Generative AI #
Probably the best-known application areas for artificial intelligence at present are generative AI. This has become popular in recent years thanks to chatbots and AI assistants such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Microsoft Copilot, Amazon Alexa, DeepSeek, Midjourney, and Perplexity. By now, …
- artificial intelligence can write texts
- artificial intelligence can paraphrase and translate texts
- artificial intelligence can create images
- artificial intelligence can create a video
- artificial intelligence can create music
How does artificial intelligence work in these cases? #
Generative artificial intelligence explained simply: By learning from large amounts of data and deriving rules, it can create new content that follows these rules. It does not create anything original or creative in the true sense of the word, but calculates probabilities as to what makes sense next. As with all existing types of artificial intelligence, this is therefore weak AI.
-
Text-based generative AI works with tokenization: The language model divides the text into tokens (e.g. characters, words and sentences), calculates a probability for each possible token and then decides which token statistically best matches the entered text description (the so-called prompt) next. In doing so, it applies the rules of the respective language.
-
AI can create images using diffusion models: The model starts with a completely noisy, random image from which it gradually removes the noise. An encoder matches the text description with suitable image elements that were contained in the model’s training material. The pixels are changed until a sharp image is created that fits the prompt statistically well.
As you can see, generative AI is strongly oriented towards the formulation of the text description entered. A prompt should therefore provide the AI model with a precise description with context, format specifications and styles in order to achieve the best possible result. Prompting is therefore a key skill when dealing with modern AI.

The advantages of AI at a glance #
Some of the advantages of AI systems for companies have already been mentioned in the course of this article. Here is an overview of the most important points:
- Automation of rule-based tasks
- Faster and more comprehensive analysis of large amounts of data
- Improved basis for decision-making
- Avoidance of human error
- Consistent results and availability around the clock
What are the risks of artificial intelligence? #
We are still a long way from the horror scenario of a hostile artificial intelligence taking over the world and turning against humans. So far, there is only weak AI that needs instructions and training from humans and will not simply take on a life of its own. Nevertheless, artificial intelligence carries the risk of leading to undesirable results or even being misused for criminal purposes.
The biggest problems surrounding artificial intelligence are
Incorrect answers due to faulty data
Hallucinating and inventing facts
Discriminatory decisions
Disinformation and fraud through deepfakes
High energy consumption of AI data centers
Data protection and dependence on tech giants
Best practices for dealing with AI in companies #
According to an EY survey , more than half of European companies are already achieving measurable benefits through the use of AI – including increased productivity, time savings, cost reductions and error reduction.
In order to take advantage of the economic opportunities and use artificial intelligence in your company sensibly and safely, a few principles have proven their worth:
- Human control: Artificial intelligence should support decisions, but not make them alone. You should not simply believe the results, but always question and check them.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate the framework conditions for the use of AI to your employees. This will help you avoid creating a shadow IT that you know nothing about. The interaction with AI must also be made clear to customers.
- Further training: AI expertise is increasingly becoming a success factor. Make your employees fit for prompting and clarify the following questions with them: How does artificial intelligence work and where is artificial intelligence used?
- Data sovereignty: If you want to use AI without compromising on data protection , it is worth running an AI model on your own servers or at least using cloud platforms within the EU.
- Compliance: Make sure that the AI systems in your company meet all applicable laws and compliance guidelines, especially the EU AI Act, because in case of doubt you will be liable.
What is the EU AI Act? #
The European Union’s AI Act is the world’s first law for the comprehensive regulation of artificial intelligence. It came into force on August 1, 2024 and will be fully applicable from August 2, 2026. The EU AI Act divides AI systems into four basic risk classes, to which different rules apply:
- Inadmissible risk: Prohibited are, for example, social scoring, real-time biometric monitoring or manipulative behavior control because they are not compatible with the protection of fundamental rights.
- High risk: The use of AI is strictly regulated in areas such as application procedures, lending and medical diagnoses. There are high requirements in terms of data quality, transparency, human supervision and documentation.
- Limited risk: As soon as humans interact with AI (e.g. chatbots), they must be informed and AI-generated content must be labeled as such.
- Minimal risk: AI applications such as spam filters, spell checkers or automatic text suggestions in search engines are not subject to any additional obligations.
The providers and operators of the systems are liable for any violations of the law and damage caused by AI applications up to 15 million euros or 3 percent of their global annual turnover.
Use artificial intelligence safely with SeaTable #
As an AI no-code platform, SeaTable enables AI-supported automations with which you can make your data management more efficient. Evaluating, modifying and expanding data records, translating texts and extracting relevant information from documents – all this is possible with the AI functions.
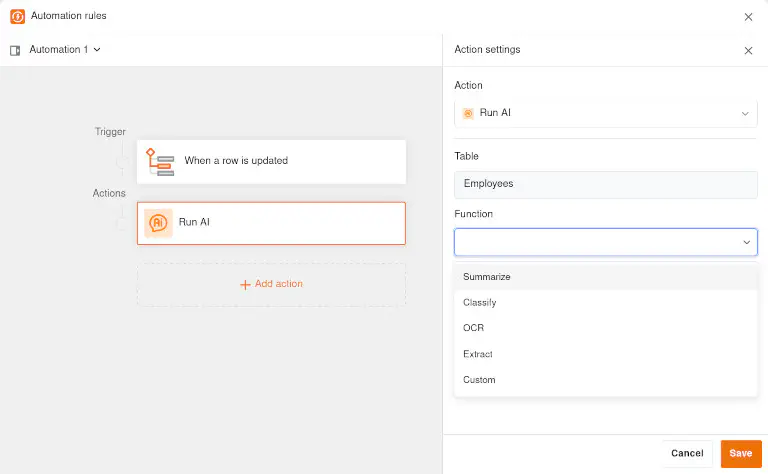
And without any worry lines when it comes to data protection: In addition to Gemma 3, SeaTable will in future support other AI models from various providers that are operated in German data centers in compliance with the GDPR. The data exchange between SeaTable Cloud and the language models is encrypted.
For full control, self-hosters can of course also use AI models in their own infrastructure. SeaTable AI , a component of SeaTable Server , is based on LiteLLM and thus supports the connection of a large number of models with an OpenAI-compatible API.
Conclusion: AI is a tool – not a replacement for human intelligence #
Artificial intelligence is probably the most powerful technology of our time. It can optimize, automate and accelerate processes, calculate with vast amounts of data and provide new insights – which makes it very valuable for companies. Nevertheless, artificial intelligence is still miles away from being a thinking being. It can imitate human abilities, but must be developed, trained and controlled by humans.
The responsible use of AI will determine whether it becomes an advantage or a problem. If you use artificial intelligence as a tool for your work, you should proceed wisely, transparently and in accordance with the rules. This will allow you to benefit from increased efficiency and productivity gains in the long term.
Frequently asked questions about AI #
How advanced is artificial intelligence today?
How does artificial intelligence work?
What is generative AI?
Where is artificial intelligence used?
What problems can artificial intelligence bring?
TAGS: Digital Transformation Data Management & Visualisation Integrations & Automations
