Most people deal with data every day that needs to be managed effectively. A supermarket owner has to keep track of inventory, an editor-in-chief needs to monitor all publications, and a hairdresser manages client appointments. In nearly every profession, data plays a role. The best way to manage large amounts of information is with databases. But what exactly is a database, what are the advantages, and why is a simple spreadsheet usually not enough?
Database Basics #
What Is a Database? #
At its core, a database is simply a logical collection of data. It’s called logical because a database is designed to bring order to a large volume of data. When we talk about data, we mean all types of information—email addresses, images, texts, numbers, or any other data type you can think of.
Types of Databases #
There are many ways to structure databases. Here’s a brief explanation of the five main types:
- Hierarchical Database: Uses a hierarchy to structure data.
- Network Database: Similar to the hierarchical type, but allows a child record to connect with multiple parent records, enabling two-way relationships.
- Object-Oriented Database: Stores information as objects.
- Relational Database: Table-oriented, with each record linked to every other record.
- Non-relational Database (or NoSQL database): Uses various formats like documents, graphs, etc., offering great flexibility in database design.

Relationships are the big advantage of relational databases.
Advantages of Databases #
Now that you understand what databases are, you might still wonder: Why should I use a database? What makes a database so much better than just listing information?
- Databases can easily handle multiple users.
- Databases are highly reliable, storing information accurately.
- Databases avoid redundant information.
- Databases process information powerfully and intelligently.
- Databases are scalable.
- Databases can handle huge amounts of information.
Even if you don’t (yet) need to process massive amounts of data, the advantages of databases are noticeable even with smaller datasets. Because you can process almost unlimited data, a well-designed database can serve you for years and will scale as you grow.

Where Spreadsheets Fall Short Compared to Databases #
1. Limited Storage Capacity #
Imagine you’ve started a business. Besides your physical store, you decide to sell your products online. At first, you get 2 to 4 orders a day, so it’s easy to record order info in a spreadsheet. But as you run ads and business booms, your order volume rises and you add more products.
The sheer amount of information you need to process daily can overwhelm a spreadsheet like Excel. The file becomes sluggish or freezes because the storage capacity is simply too low. One of the advantages of databases, as mentioned above, is that they offer much greater storage capacity and can easily scale with your business. They are much more scalable than simple spreadsheets.
2. Handling Multiple Users at Once #
As your order volume grows, so does your team. In the first months, you hire five new employees. Unlike most spreadsheets, databases are designed for multiple users to collaborate simultaneously. Querying, searching, and editing the database at the same time is easy, and built-in mechanisms prevent conflicts between users’ changes.
You can also assign access and editing rights based on each employee’s role or responsibility. While newer cloud-based spreadsheets solve some problems, they usually lack the granular access control that a database provides.
3. Reliability and Avoiding Human Input Errors #
We’re all human—and humans make mistakes. The lack of structure in a simple spreadsheet makes it prone to human input errors. In a database, there are specific rules that must be followed when users enter or change data. For example, you can define the required length of a numeric code, ensuring users don’t forget a digit when entering account numbers.
Databases also protect against accidental data deletion. You can view change histories and undo deletions with just a few clicks.
4. Redundant Data #
Databases let you make information easily accessible for future use. To ensure this simplicity, you should make sure that each data unit exists only once. If the same data exists in multiple places, that’s redundant data. If a database has redundant data, it’s a sign of poor database design.
Eliminating redundancy not only keeps things clear and simple, but is also helpful when you need to update information. For example, if a customer’s address changes, you only need to update it once in the customer database. Since each order is linked to a unique customer number, all orders reference the updated customer record.
In some cases, redundancy is intentional—especially in relational databases like in a data warehouse or business intelligence environments, to speed up complex SQL queries.
5. Performance #
Databases are built to make data retrieval easy and powerful. You can create database queries and filter records to answer specific questions, such as:
- Which region do customers who buy product XY come from?
- How many times was product XY sold in December?
- How do customers find my website?
The results of such queries can be saved as views, which are subsets of the database. These views help specific user groups find the data most relevant to them.
Databases Are Becoming More User-Friendly #
In the past, you had to learn programming languages to create the data queries described above. Today, many database systems like SeaTable come with an intuitive graphical user interface. This allows even beginners to use databases right away and improve their workflow.
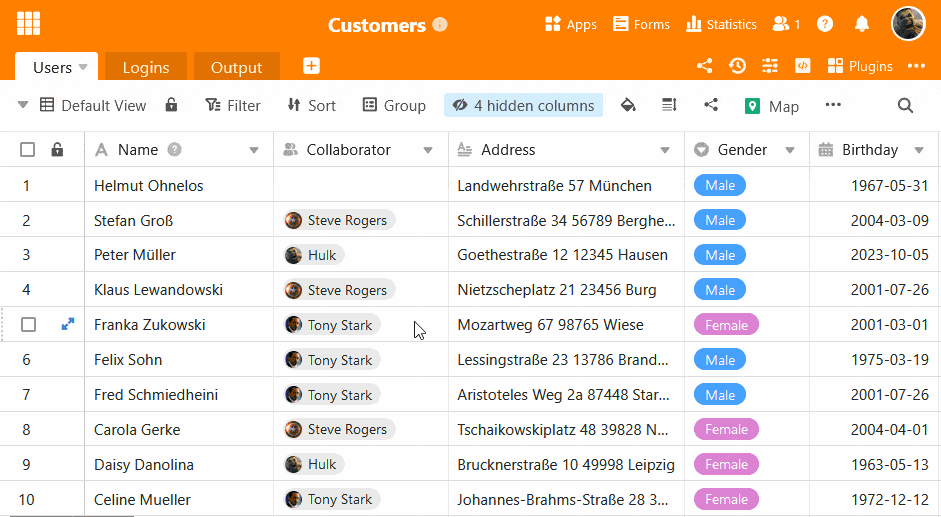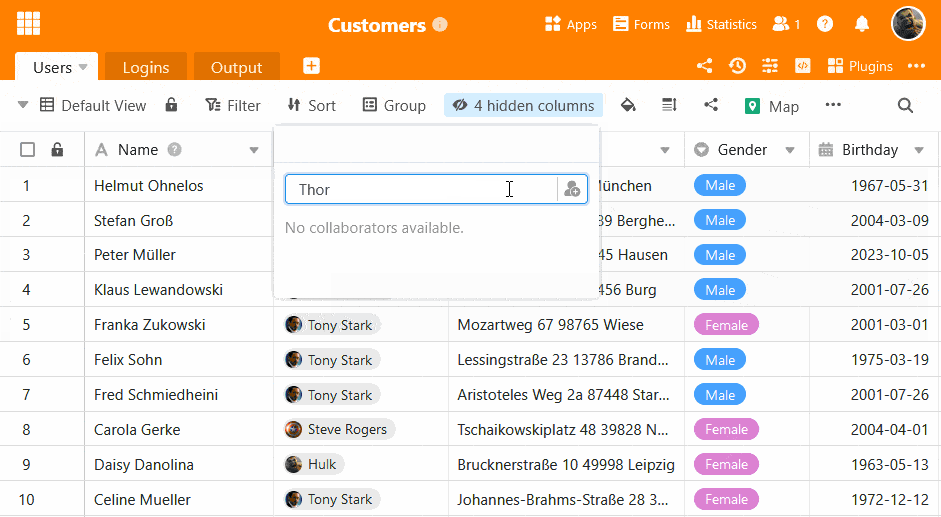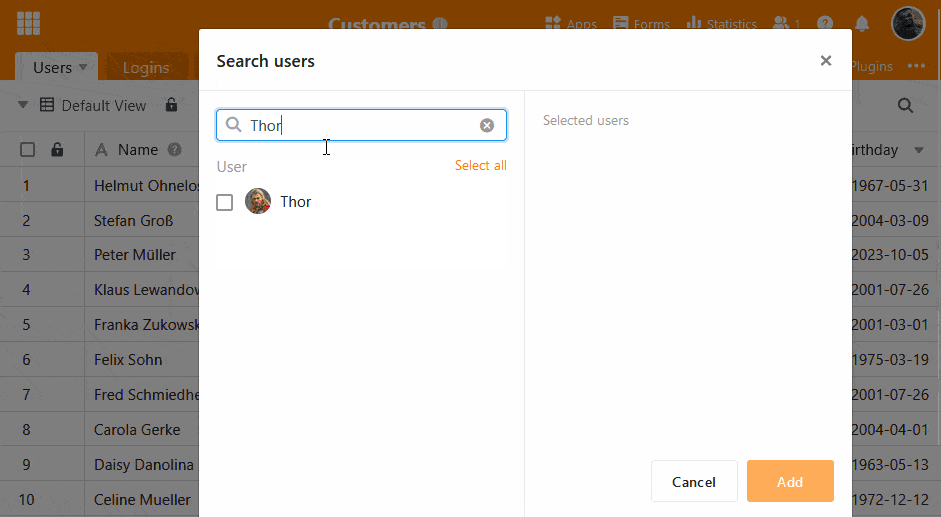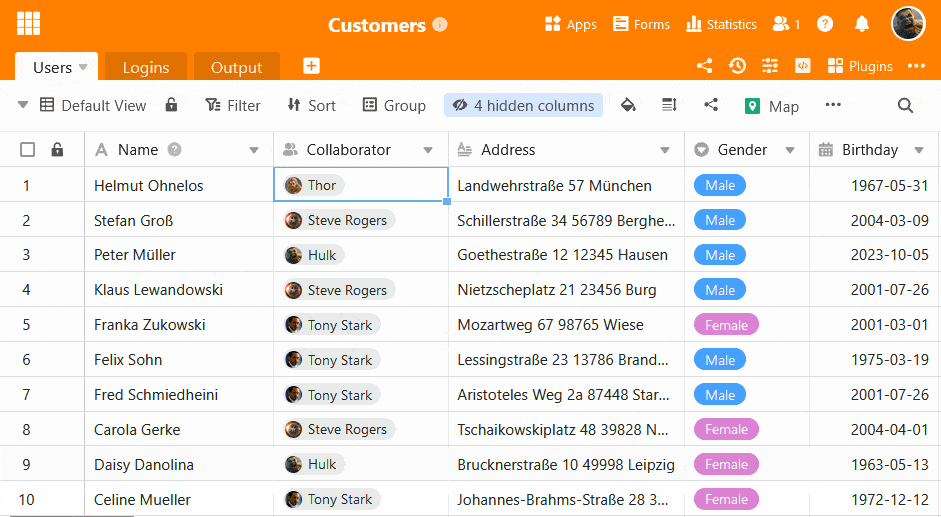
Unlike classic databases, SeaTable has a graphical user interface.
How to Easily Build Your Own Database #
The advantages of databases make sense to you, but the idea of building your own database still seems daunting? Good news: You don’t need special skills anymore. With SeaTable, you can easily assemble the building blocks of your own database—no programming required.
Check out many examples of how to use SeaTable in our template library . There you’ll find examples for marketing, sales, project management, software development, HR, and more. We’ve even prepared a 7-part product introduction on our YouTube channel, guiding you through the entire process of creating a SeaTable base.
Take advantage of a database and say goodbye to confusing spreadsheets today! Click here to register for free!
TAGS: