Say Goodbye to coding - with Low Code and No Code #
Have you ever wished you could develop your own software solutions with just a few clicks, without having to write line after line of code? Imagine how easy and fast software development would suddenly be for you! Does it feel like science fiction? But it’s not: Take a look at the world of low-code development with us! In the following article, we also look at the difference between low code and no code and clarify what a no-code/low-code platform is.
What is low code? #
Low code is the technical term for development methods in which programming is no longer carried out using text-based programming languages, but on the basis of visual aids. Intuitive graphical tools and ready-made modules make it possible to create applications with little manual programming effort.
Software development is always strenuous, time-consuming and requires the skills of experienced developers. Low code development promises to speed up and simplify this laborious process."
Christoph Dyllick-Brenzinger, CTO of SeaTable
What is a low code platform? #
A low-code platform is a development environment in which you can create software applications largely without text-based programming. Instead of writing hundreds of lines of code, you work with a visual user interface on which you can assemble prefabricated building blocks in a modular way. These building blocks represent specific functions or logic that you would normally have to implement using conventional programming.
5 main features of low code platforms #
The core features of a low-code platform can be summarized using these characteristics:
- Visual development environment: Instead of writing complex code line by line, you use a graphical user interface where you can simply drag and drop pre-built components together.
- Reusable building blocks: Low code platforms offer a variety of pre-built elements, modules and templates that you can combine, reuse and customize to your needs over and over again.
- Manual code integration: Although the focus is on visual development, many low code platforms also allow you to integrate your own scripts. This gives you the opportunity to implement custom functions that go beyond the standard options.
- Rapid deployment: Lowcode allows you to develop and deploy software prototypes and working applications in a very short time, which is especially beneficial in agile development environments.
- Cloud-based use: In most cases, software applications are developed, deployed and used conveniently via a web browser. However, some low-code platforms can not only be used in the cloud, but can also be installed locally as an on-premises system.
What is No Code? #
No Code goes one step further: unlike low-code platforms, a no-code platform is aimed at users without any programming knowledge. In the fully visual development environment, you can create applications mostly by drag-and-drop without having to write a single line of code. No Code is therefore ideal for creating simple applications and automated workflows . The focus here is clearly on speed and user-friendliness; the integration of self-written code is not provided for.
Low code vs. no code #
However, the transitions between the two approaches are fluid. For this reason, many tools cannot be clearly assigned to the no code or low code area. The main difference between low code / no code lies in the target group, the flexibility and the complexity of the applications.
Target group: A low code platform is aimed at developers who want to enjoy fast, modular development but still want the option of implementing user-defined functions through manual programming. No Code, on the other hand, is mainly aimed at users with no prior technical knowledge.
Flexibility: A low-code platform offers more flexibility and customization options, as developers can intervene in the code and program their own components if required. No-code platforms are designed more for standard solutions and offer less scope for individual customization, as they specify a large part of the design.
Complexity of applications: Low-code allows you to create more complex applications that can be extended at will, while no-code is more suitable for simple, off-the-shelf solutions.

Comparison of the advantages of no-code and low-code platforms #
Common advantages of low code and no code #
Low code and no code have three key advantages in common:
- Accelerated development: By using visual tools and pre-built building blocks, you can build applications in a fraction of the time it would take with traditional software development.
- Collaboration: Thanks to the graphical user interface, even people without programming skills, for example Citizen Developer , can participate in the development process, provide feedback or even create their own solutions independently.
- Cost efficiency: A significantly lower time expenditure and the possibility that even less experienced developers can program productively lead to lower development costs.
The biggest advantages of low-code programming #
Low-code platforms usually offer a balance between user-friendliness and flexibility. They allow you to create applications on the fly using intuitive tools and off-the-shelf components, while keeping the option open to integrate custom code if needed. This allows you to tailor low-code applications precisely to the needs of your business.
Low-code programming gives you the ability to make specific customizations to the design and add your own components via manual code. Since the underlying code is mostly standardized, you can easily extend low-code applications with your own scripts. But be careful: No-code platforms also often offer programming interfaces for the integration of external applications.
Areas of application for low-code development #
Both development methods are particularly suitable for companies that have limited developer capacities, need to react quickly to changes and are looking for an efficient way to develop customized software solutions. No code and low code are not limited to one industry or specific processes, but can be used almost universally.
Typical use cases are
- Process automation: Automate workflows and processes to increase efficiency in your company.
- Customizable off-the-shelf solutions: Drive off-the-shelf development of standard solutions that can be customized to meet the business needs of different customers or departments.
- Citizen Development: Turn today’s users into tomorrow’s developers with the help of no-code. This relieves your IT department, which can instead take on steering and strategic tasks.
- Prototypes and MVPs (Minimum Viable Products): Quickly develop ready-to-use software prototypes to test ideas and get early feedback.
“In my view, a low-code platform should be seen as a playground for trying out new solutions to digitally design and automate processes.”
Christoph Dyllick-Brenzinger, CTO of SeaTable
Should you use a low-code or no-code platform? #
The choice between low code and no code depends on your specific requirements:
- If you need a quick solution for a digital process and the application does not have highly customized requirements, a no code platform should suffice.
- However, if you need a complex, customized application that you want to develop yourself over time, a low-code platform is the better choice.
Is low-code development the future? #
In the digital era, low-code platforms are becoming increasingly important. This is because their technologies make it possible to develop software applications faster, more efficiently and with less technical expertise. Compared to traditional programming, low-code development requires only a fraction of the time to deliver the software.
Due to this unbeatable efficiency and cost savings, low-code platforms are naturally of interest to many companies and play a key role in the ongoing digitalization of business processes. It can be assumed that almost all companies and people who work with computers have a need for this type of development and problem solving.
does low-code development belong to the future?(Gehoert-der-Low-Code-Entwicklung-die-Zukunft.jpg)
At the same time, the high level of customer interest means that more and more low-code solutions are entering the market. No wonder that market analyses by Gartner show how almost 14 billion US dollars were already generated with low-code development technologies in 2021. Furthermore, Gartner assumes that by 2024, two thirds of all software developments will be attributable to low-code platforms.
Comparison of types of no-code/low-code platforms #
Most low-code providers can be summarized in four large groups. Unsurprisingly, the demand for low-code platforms is highest exactly where almost every company needs software: for websites, apps, databases and automated processes.
Website builder #
Gone are the days when you had to hire an expensive agency or web designer for a fancy website. With these low-code platforms, you can design simple websites without much programming knowledge: WordPress, Webflow, Wix, Squarespace, Framer, Dorik and many more. Some website builders such as Shopify, Sharetribe, BigCommerce or WooCommerce specialize in online stores.
App builder #
Software solutions in this category help you to create complete web applications and native apps for desktops or mobile devices. External data sources such as spreadsheets or databases are often tapped into. Low code providers in this area include Glide, AppSheet, Softr, Draftbit, Adalo and Zoho Creator.
Databases #
In every digital process, you need to capture or process data in some form. That’s why there are database-based low-code platforms that help you store and visualize your data in a structured way. The best-known providers include SeaTable, Airtable, Baserow and NoCoDB.
Automation platforms #
Automation platforms such as Zapier, make or n8n are used to exchange data between two or more applications. The logic of these solutions is always the same: First you define a trigger, i.e. an event, which then triggers your automations under certain conditions. This allows you to run even complex processes fully automatically.
In addition to these four categories, there are also more niche low-code platforms such as chatbot builders. In addition, a solution cannot always be assigned to just one category, as we will see in the following example.
SeaTable: No-code database with integrated app builder, scripts and automations #
In SeaTable, you can configure processes and applications conveniently via a graphical user interface in the browser. Thanks to the visual elements, you do not need a single line of code, which makes SeaTable a no-code solution . However, SeaTable also allows the execution of manually programmed JavaScript and Python scripts. This option is more in line with the low-coding approach, which means that SeaTable could also be described as a low-code development platform.
The classification into a category is also not clear: On the one hand, SeaTable is a no-code database in which you can store, organize and visualize almost any type of information. You can use 25 different column types, plugins such as gallery, Kanban, map or calendar, views with filter, sorting and grouping functions as well as statistics and web forms.
SeaTable also offers a No Code App Builder, which you can use to build your own apps without any programming knowledge. An app accesses the information in the database backend and displays it optimally for the end user. For the app design, there are ready-made page types with visual elements that you can simply drag and drop together.
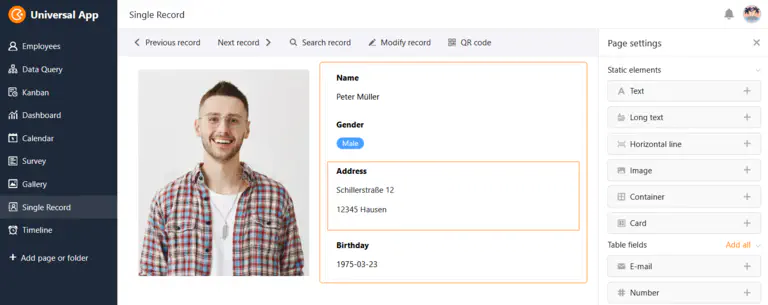
In addition, SeaTable makes it easy to create automations that save you manual clicks for the same processes over and over again and at the same time minimize the susceptibility to errors of monotonous activities. For automated processes with multiple data sources, you can also integrate SeaTable with automation platforms such as Zapier, make or n8n.
Are you already hooked and want to see for yourself? Then simply register for free for the SeaTable Cloud and try SeaTable for an unlimited time.
Conclusion: Success with no code and low code #
The platforms presented here offer valuable low-code tools to speed up and simplify application development and make it more cost-effective. It will therefore be hard to imagine the future without them. While no code opens the door to the world of software development for people without programming skills, low-code platforms offer the perfect mix of speed and flexibility for all developers who want to make their lives easier. You should consider this carefully beforehand so that you choose the right platform for your requirements.
FAQ #
What is low code?
What is the difference between low code and no code?
Is a low code or a no code platform better?